Internet Most Common Questions
- WWW: -World Wide Web is the full form of This, It used to Communicate Client to Server Network all Over Internet.
- SWITCH: – It’s Devices to Convert Single Internet Connection to Multiple Port
- ROUTER: -It Access Internet Data Pack and Convert to System Port
- IP ADDRESS: – It’s an Address of Any Internet Accessed Devices
- PORT: – Connecting Points is Called Port.
- MODEM: -It work to Get Internet Data Access to Route Systems Devices
- HTTP: – It’s Unsecured Route of Data Access for Any Websites, Websites Starts with http//www.vedantsri.net
- HTTPS: -It’s Secured Route of Data Access for Any Websites, Websites Starts with https//www.vedantsri.net
- DOMAIN: -Its Name of Any Website using Their Web Address. If https://www.vedantsri.net a Website Address Then VedantSri is Domain Name of This Website.
- DOMAIN-EXTENSION: – .com .net .co.in .in .ac.in .gov .org etc are Domain Extension of Any Websites Address.
- SERVER :- Data Stored Point/Place are Called Server. Server Has Data Stored When User What to Get/Access/Search Then Server Provides/Display Data Related User Search/Need.
- CLIENT :-Users/Operator Systems are Called Client System. This system Used to Search or Access SERVER Data on Client System.
- NETWORK :-A Connection Among Servers and Clients System Called Network.
- TYPES OF NETWORK :- There are 2 Types of Network. Wired Network and Wireless Network.
- Bandwidth: The maximum rate of data transfer across a given path. It is usually measured in bits per second (bps) and indicates the capacity of a network connection.
- Cookie: A small piece of data stored on the user’s computer by the web browser while browsing a website. Cookies are used to remember information about the user, such as login status or site preferences.
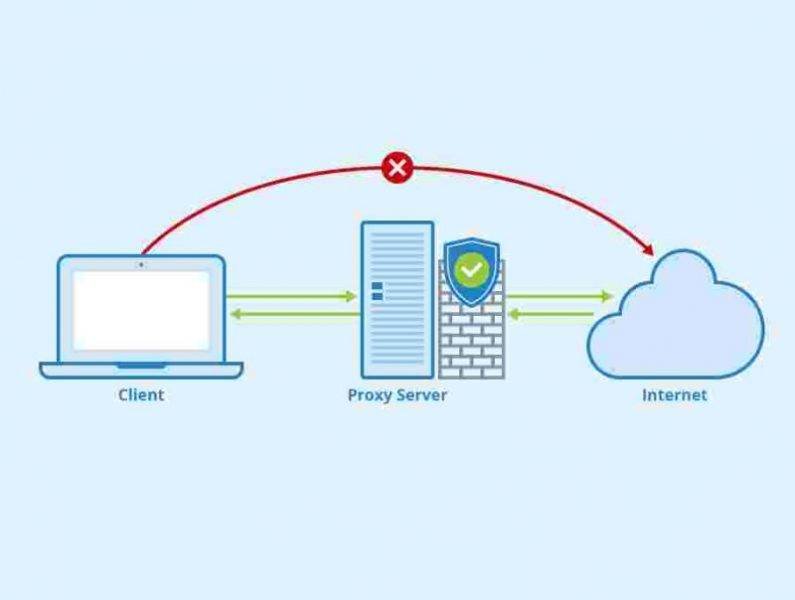
- Firewall: A network security system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. It establishes a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks.
- ISP (Internet Service Provider): A company that provides individuals and organizations access to the internet and other related services such as web hosting and email.
- Latency: The delay before a transfer of data begins following an instruction for its transfer. It is typically measured in milliseconds (ms).
- Phishing: A method of trying to gather personal information using deceptive emails and websites. It often involves tricking users into providing sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details.
- SSL (Secure Sockets Layer): A standard security technology for establishing an encrypted link between a server and a client—typically a web server and a browser. SSL ensures that all data passed between the web server and browsers remain private.
- URL (Uniform Resource Locator): The address of a web page on the internet. A URL consists of a protocol, domain name, and possibly a path and query string.
- VPN (Virtual Private Network): A service that encrypts your internet traffic and protects your online identity by masking your IP address. VPNs are used to secure internet connections and protect data.
- Wi-Fi: A technology for wireless local area networking with devices based on the IEEE 802.11 standards. It allows devices to connect to the internet and communicate wirelessly within a local area.
- What is the Internet? Answer: The Internet is a global network of interconnected computers that communicate through standardized protocols to share information and resources.
- How does the Internet work? Answer: The Internet works by transferring data in packets using the TCP/IP protocol. These packets travel through routers and servers to reach their destination.
- What is DNS? Answer: The Domain Name System (DNS) translates domain names into IP addresses, allowing browsers to load Internet resources.
- What is a web browser? Answer: A web browser is a software application used to access and view websites on the Internet. Examples include Chrome, Firefox, and Safari.
- What is a URL? Answer: A Uniform Resource Locator (URL) is the address used to access resources on the Internet, such as web pages, images, and videos.
- What is cloud computing? Answer: Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—servers, storage, databases, networking, software—over the Internet (“the cloud”).
- What is malware? Answer: Malware is malicious software designed to harm, exploit, or otherwise compromise a computer system.
- What is SEO? Answer: Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the practice of optimizing web content to increase its visibility and ranking in search engine results.
- What is social media? Answer: Social media refers to online platforms where users create, share, and interact with content, such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
- What is e-commerce? Answer: E-commerce, or electronic commerce, is the buying and selling of goods and services over the Internet.
- What is digital marketing? Answer: Digital marketing is the promotion of products or brands via electronic media, primarily on the Internet, including SEO, social media, email, and online advertising.
- What is IoT? Answer: The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical objects (“things”) embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet.
- What is blockchain? Answer: Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across many computers in such a way that the registered transactions cannot be altered retroactively.
- What is cloud computing? Answer: Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services—such as storage, databases, servers, networking, software, and analytics—over the Internet (“the cloud”). Cloud services enable users to access and utilize resources on-demand, typically managed by third-party providers, without the need for physical infrastructure or hardware maintenance.
- What is cybersecurity? Answer: Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, programs, and data from digital attacks, theft, or damage. It encompasses preventive measures, detection, response to threats, and recovery from cyber incidents to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information and systems.
- What is net neutrality? Answer: Net neutrality is the principle that Internet service providers (ISPs) should treat all data on the Internet equally, without discriminating or charging differently based on user, content, website, platform, application, or method of communication. It advocates for an open and free Internet where users have equal access to all content and services.
- What is streaming? Answer: Streaming refers to the continuous transmission of audio, video, or multimedia content over the Internet in real-time. It allows users to consume content instantly without downloading large files. Popular streaming services include Netflix, YouTube, Spotify, and Twitch.
- What is virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR)? Answer: Virtual reality (VR) refers to a simulated experience that immerses users in a computer-generated environment, typically viewed through VR headsets. Augmented reality (AR) overlays digital information, such as images or text, onto the real-world environment viewed through devices like smartphones or AR glasses.
- What is broadband Internet? Answer: Broadband Internet refers to high-speed Internet access that is faster and more reliable than traditional dial-up connections. It enables faster data transmission and supports bandwidth-intensive activities such as streaming videos, online gaming, video conferencing, and large file downloads.
- What is encryption? Answer: Encryption is the process of encoding information (data) in such a way that only authorized parties can access and understand it. It uses cryptographic algorithms to convert plaintext (readable data) into ciphertext (encrypted data), which can be decrypted back into plaintext using a key or password.
- What is cyberbullying? Answer: Cyberbullying refers to the use of digital communication tools and platforms (e.g., social media, messaging apps) to harass, intimidate, or threaten individuals or groups. It may involve spreading rumors, sharing embarrassing photos or messages, or engaging in online harassment, causing emotional distress and harm.
- What is a server? Answer: A server is a computer or system that provides resources, services, or data to other computers (clients) over a network. Servers can host websites, store files, manage databases, process requests, and perform various tasks to enable communication and access to resources on the Internet.
- What is a blog? Answer: A blog is a type of website or online platform where individuals or organizations publish regular entries (posts) in reverse chronological order. Blogs often focus on specific topics or niches and allow readers to comment and interact with the content through comments or social media sharing.
- What is a digital footprint? Answer: A digital footprint refers to the trail of data left behind by a person’s online activities. It includes information such as social media posts, online purchases, browsing history, and interactions with websites. Digital footprints can have implications for privacy, reputation, and security.
- What is a CAPTCHA? Answer: CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart) is a security mechanism used to determine whether a user is human or a bot. It typically presents challenges that are easy for humans to solve but difficult for automated systems, such as distorted text or image recognition tasks.
- What is a digital divide? Answer: The digital divide refers to the gap between individuals or communities that have access to digital technologies (such as the Internet) and those that do not. It encompasses disparities in access to hardware, software, Internet connectivity, and digital literacy, impacting opportunities for education, employment, and social participation.
Important link of Internet Most Common Questions
- Visit at – https://www.corelclass.com
- Read Also it – https://msexcelclass.com/
- Also, Read- Tally Course Fees, Duration, Scope, Syllabus, Admission, Institutes
- Also Read – CCC Course Fees, Syllabus, Duration, Scope, Jobs, and Institute
- Important Link – DFA Course Fees, Syllabus, Duration, Scope, Jobs, and Institute
- Visit – https://mswordclass.com/